In the face of soaring electricity costs and frequent power disruptions, Pakistani households and businesses are increasingly turning to solar energy solutions as a practical and cost-effective alternative. With electricity prices in Pakistan projected to rise by 25% over the next eight years, reaching an average tariff of Rs29.70 per unit by 2034, the economic case for solar power has never been stronger . This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about harnessing solar energy to significantly reduce your electricity bills in 2026, providing both immediate savings and long-term energy security for your home or business.
Solar power isn’t just about cost savings—it represents a fundamental shift toward energy independence and sustainability. Pakistan has seen an extraordinary surge in solar adoption, with the technology expected to become the country’s second-largest source of power generation by June 2026, contributing 19% of the nation’s electricity . This remarkable growth is fueled by declining solar energy costs, improved technology efficiency, and supportive policies like net metering that make solar investments increasingly attractive for ordinary Pakistanis.
Table of Contents
Pakistan’s Solar Energy Potential and the 2026 Outlook
The Rising Cost of Conventional Electricity
The electricity crisis in Pakistan has reached a tipping point. Over the past three years, electricity tariffs have surged by nearly 50%, jumping from Rs16.77 per unit in FY2022 to Rs24.88 per unit in FY2025 . This dramatic increase is largely attributed to currency depreciation, which has triggered inflation and led to higher power purchase rates. The impact has been particularly severe on the industrial sector, where rising energy costs have made Pakistani businesses less competitive, leading to a noticeable decline in industrial power consumption from 34 billion units in FY2022 to 28 billion units in FY2024 .
Despite these challenges, there’s a silver lining. The power division expects a slower tariff increase in the coming years, with rates projected to rise by 25% to 30% over the next decade, compared to more than 260% in the past ten years . This moderation, combined with Pakistan’s shift toward cleaner energy sources, presents a unique opportunity for consumers to take control of their energy costs through solar power.
Solar Energy: From Alternative to Mainstream
Solar power is rapidly transitioning from an alternative energy source to a mainstream power solution in Pakistan. Official projections indicate that solar will become Pakistan’s second-largest source of power generation by June 2026, following hydropower, with an expected contribution of 8,444MW or 19% of the total electricity . The growth of solar net metering has been particularly impressive, with an anticipated contribution of 7,794MW to the national grid by June 2026 .
This solar revolution isn’t happening in a vacuum. Pakistan imported a staggering 22 gigawatts worth of solar panels in 2024 alone—more than Canada has installed in total and more than the UK added in the past five years . This massive adoption is being driven by both economic necessity and technological advancement, as Pakistani households and businesses recognize the long-term benefits of generating their own electricity.

Understanding the Financial Benefits of Solar Energy
Significant Reduction in Electricity Bills
The most immediate benefit of installing a solar power system is the substantial reduction in your monthly electricity bills. A well-sized solar system can typically reduce your electricity bill by 50% to 80%, translating to thousands of rupees in monthly savings . The exact savings depend on several factors, including your energy consumption patterns, the size and efficiency of your solar system, and your ability to shift energy-intensive activities to daylight hours.
The financial advantage of solar becomes even more compelling when considering the projected increases in conventional electricity costs. With electricity prices expected to reach Rs29.70 per unit by 2034, the value of every unit of solar energy you generate will continue to increase over time . This makes solar power not just a cost-saving measure today, but a strategic hedge against future electricity price volatility.
Favorable Return on Investment and Payback Period
Solar power systems represent a significant upfront investment, but one that typically offers an excellent return compared to many traditional investments. While payback periods vary depending on system size, energy consumption, and local conditions, on-grid residential systems in Pakistan often see paybacks in 3-6 years . Commercial projects that offset peak-demand charges may achieve even faster returns.
To put this in perspective, consider a simplified example: A 5kW on-grid system with an expected annual energy production of 7,000 kWh. If your current electricity tariff is PKR 30 per kWh and the system costs PKR 170,000, your first-year energy savings would be approximately 7,000 kWh × PKR 30 = PKR 210,000 . This would result in a simple payback period of less than a year in this aggressive example, though in practice you should include more conservative yield assumptions, degradation, and any financing costs for accurate planning.
Increased Property Value and Solar Energy Independence
Beyond direct savings on electricity bills, solar power systems can significantly enhance your property’s market value. In today’s eco-conscious market, homes with solar energy systems are more attractive to potential buyers, who recognize the value of lower energy costs and environmental benefits. There is good evidence to suggest that customers will be willing to pay a premium for properties that have low energy consumption .
Perhaps equally valuable is the energy independence that solar power provides. For many Pakistanis, especially those in areas with frequent load-shedding, solar energy offers a sense of security and reliability that the national grid cannot always guarantee . With a solar system in place, you can reduce your dependence on the national grid and enjoy uninterrupted power supply—particularly valuable for businesses that cannot afford downtime and for families who need a stable energy source for daily life.
Key Components of a Solar Energy System
Solar Panels: Types, Efficiency, and Pricing
Choosing the right solar panels is crucial for maximizing your system’s performance and return on investment. The Pakistani market offers a wide range of options, with prices typically ranging from PKR 26 to PKR 37 per watt depending on the brand, technology, and efficiency . The main types of solar panels available include:
- Monocrystalline panels: These are generally more efficient and space-efficient, making them ideal for roofs with limited space. Brands like LONGI offer models with efficiencies that make them particularly suitable for Pakistani conditions.
- Polycrystalline panels: These are typically more budget-friendly but slightly less efficient and require more space for the same power output.
- N-Type panels: These newer technology panels, such as the Doart N-Type 590 Watt panel priced at PKR 16,815, offer better performance in high-temperature conditions and lower degradation rates .
When selecting panels, consider not just the initial cost but also factors like temperature coefficients (how well panels perform in Pakistan’s hot climate), warranty terms, and the manufacturer’s track record in the local market.
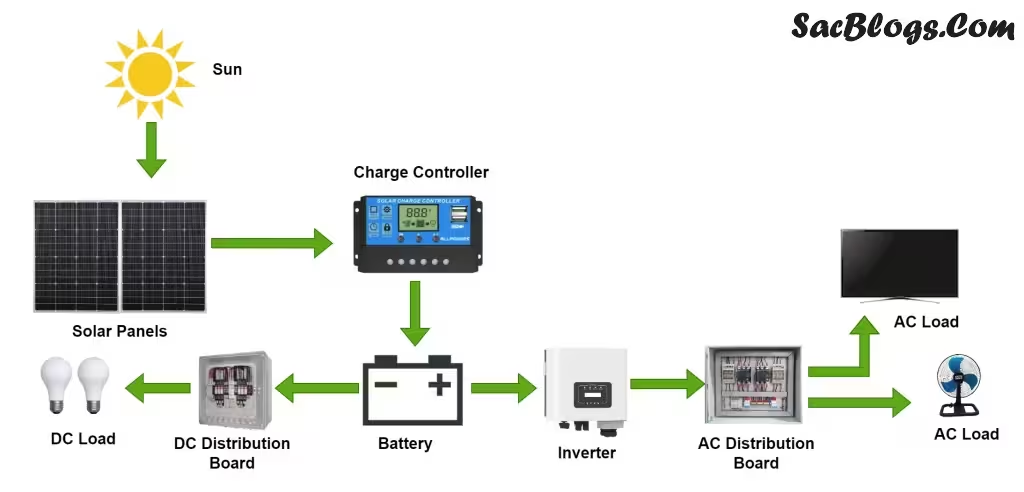
Inverters: The Heart of Your Solar Energy System
Inverters play a critical role in your solar system, converting the DC electricity generated by your panels into AC power that can be used in your home or business. The choice of inverter depends on your system design and specific needs:
- On-grid inverters: These are used in systems that remain connected to the national grid without battery backup.
- Hybrid inverters: These allow you to integrate battery storage and grid connection, providing backup power during outages while still enabling net metering.
Inverter prices in Pakistan vary significantly based on capacity and features. For example, a 6kW Knox hybrid inverter costs approximately PKR 135,000-158,000, while a 6kW Crown Elego hybrid inverter is priced around PKR 205,000 . When selecting an inverter, consider factors like efficiency ratings, warranty terms, after-sales service, and compatibility with your planned system configuration.
Mounting Structures and Balance of System
The mounting structure is what securely attaches your solar panels to your roof or ground area. In Pakistan’s diverse climate conditions, it’s essential to choose mounting materials with appropriate galvanization standards to prevent corrosion and ensure long-term durability . Wind-rated racking is particularly important in areas prone to strong seasonal winds.
The balance of system components—including cables, connectors, DC isolators, surge protection devices, and earthing systems—may seem less glamorous than panels and inverters, but they are equally important for safety and performance. Always insist on appropriately sized, flame-retardant cables and quality protection devices to ensure your system operates safely for years to come.
Planning Your Solar Installation: A Step-by-Step Guide
Energy Assessment and System Sizing
Properly sizing your solar system is the foundation of a successful installation that meets your energy needs and budget constraints. Follow these steps to determine your optimal system size:
- Analyze your electricity consumption: Collect 12-24 months of electricity bills to understand your household or business’s energy usage patterns . Look for seasonal variations and identify opportunities to shift usage to daylight hours.
- Calculate your daily energy needs: Divide your monthly kWh usage by 30 to determine average daily consumption. This forms the basis for your system sizing.
- Consider your energy goals: Decide what percentage of your electricity consumption you want to offset with solar. While 100% offset is possible, it may not be cost-effective due to the higher cost of battery storage compared to grid electricity.
As a reference point, typical system sizes and their outputs include:
- A 5 kW rooftop system: typical annual yield 6,000-8,000 kWh
- A 10 kW system: 12,000-16,000 kWh per year
- A 5kW solar system can power essential household appliances, including lights, a fridge, a TV, washing machine, and a small air conditioning unit
Selecting the Right Type of Solar Energy System
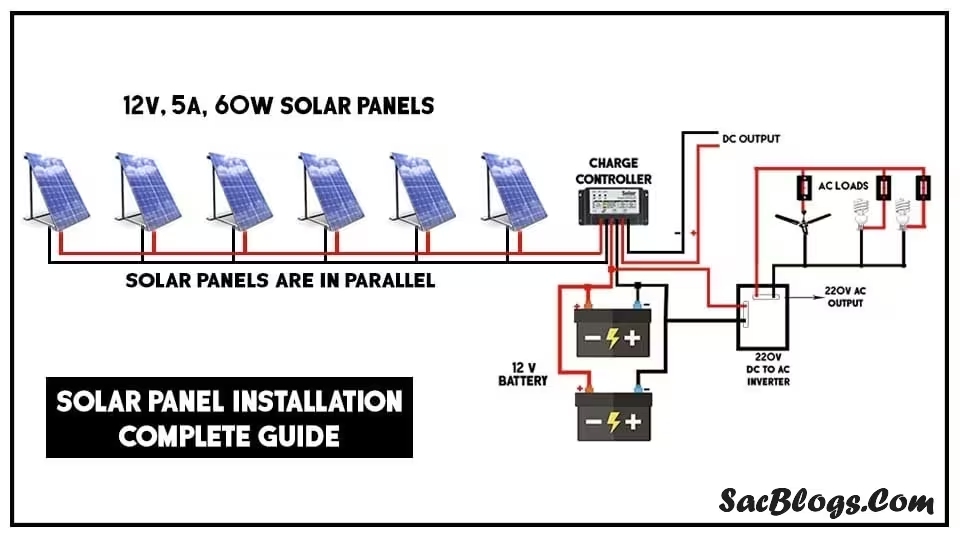
Different energy needs and budgets call for different system configurations. The main types of solar systems available in Pakistan are:
- On-grid systems: These systems are connected to the national grid and are ideal for urban areas with relatively stable grid power. They allow you to benefit from net metering, where excess electricity is exported to the grid in exchange for credits on your electricity bill. On-grid systems typically have the lowest upfront cost since they don’t require batteries .
- Hybrid systems: These combine solar panels with battery storage and grid connection, offering the best of both worlds—energy savings through net metering plus backup power during outages. Hybrid systems are increasingly popular in areas with frequent load-shedding .
- Off-grid systems: These completely disconnect from the national grid and rely entirely on solar power and battery storage. While offering complete energy independence, they come with significantly higher costs due to the extensive battery bank required .
Choosing a Reputable Installer
The expertise of your solar installer significantly impacts every aspect of your system’s performance and longevity. When evaluating potential installers, consider the following criteria:
- Engineering capability and documented references: Ask for examples of previous installations and speak with past clients about their experience .
- Local presence and service network: Ensure the company has a solid local presence that can provide timely maintenance and support when needed.
- Clear contract terms: The contract should clearly outline project milestones, payment schedules, warranty responsibilities, and performance guarantees .
- Transparent pricing: Request an itemized quotation that breaks down costs for equipment, labor, and any additional services.
A professional installer will also manage the net metering application process with your local distribution company (DISCO), which can be complex and time-consuming.
Financial Planning and Incentives for Solar Energy Adoption
Understanding the Costs: A Detailed Breakdown
The cost of installing solar panels in Pakistan varies depending on system size, component quality, and installation complexity. Here’s a general overview of current pricing:
| System Size | Price Range (PKR) | Suitable For |
|---|---|---|
| 3kW | 290,000 | Small homes with basic electricity needs |
| 5kW | 450,000-600,000 | Medium-sized homes with moderate AC use |
| 10kW | 900,000 | Large homes or small businesses |
| 15kW | 1,300,000 | Large homes with central AC or medium businesses |
| 20kW | 1,800,000 | Commercial establishments or large villas |
These costs typically include solar panels, inverters, mounting structures, balance of system components, and installation labor. Additional costs may apply for battery storage (typically PKR 200,000 to PKR 400,000) , structural reinforcements, or electrical panel upgrades.
Net Metering: Getting Credit for Excess Power
Net metering is a crucial policy that makes solar investments economically viable for most Pakistani consumers. Under net metering, any excess electricity your solar system generates during the day is exported to the grid, and you receive credits that offset your consumption from the grid at night or during cloudy days.
The application process for net metering involves:
- Submitting an application to your local DISCO along with required documents, including system design, component specifications, and installer credentials.
- Waiting for approval and installation of a bidirectional meter that can measure both import and export of electricity.
- Scheduling inspections as required by your DISCO to ensure the system meets safety and technical standards.
The number of net metering consumers in Pakistan is expected to grow by 197,655 during FY2025-26, reflecting the rapidly growing adoption of this mechanism .
Upcoming Policy Changes and Their Implications
While solar adoption continues to grow, potential policy changes could affect the economics of going solar in 2026. The Federal Board of Revenue (FBR) has proposed increasing the General Sales Tax (GST) on imported solar energy from 10% to 18%, starting January 2026 . If implemented, this tax hike could increase the cost of solar systems by approximately 6-8%, potentially adding PKR 50,000-100,000 to the cost of a typical residential installation.
This proposed tax has drawn criticism from industry stakeholders like the Pakistan Solar Association (PSA), which warns that it would “make solar energy less affordable for consumers and damage the confidence of investors and stakeholders in this vital industry” . For consumers considering solar, this potential price increase creates additional incentive to move forward with installations sooner rather than later.
The Future of Solar Energy in Pakistan
Technological Advancements and Trends
The solar energy landscape is continuously evolving, with several key trends likely to shape the market in 2026 and beyond:
- Increasing panel efficiency: Ongoing research and development are steadily pushing commercial panel efficiencies higher, meaning future systems will generate more power from the same roof area.
- Advancing battery technology: As battery costs continue to decline and performance improves, energy storage will become increasingly accessible to average consumers, enhancing energy independence.
- Smart energy management: Integration of smart technologies that optimize energy usage based on generation patterns, tariff schedules, and consumption habits will maximize the value of solar investments.
- Growth in electric vehicles: With Pakistan’s goal to convert 30% of all vehicles to electric by 2030, and companies like BYD and Jolta Electric rolling out EV options, solar-powered charging will become an increasingly attractive option .
Pakistan’s Clean Energy Transition
Solar energy is playing a pivotal role in Pakistan’s broader transition toward cleaner energy sources. By 2034, clean-fuel generation is expected to account for 66% of total generation, up from 46% in FY2025 . This shift is part of Pakistan’s commitment under the Paris Agreement, which includes a target of 50% reduction from its projected 2030 emissions, with 15% of that unconditionally promised .
The government’s ambitious Ten Billion Tree Tsunami program, building on the successful Billion Tree Tsunami in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, symbolizes this growing climate consciousness and application of state capacity toward environmental regeneration . As solar energy becomes increasingly central to Pakistan’s energy mix, it represents not just individual savings but a collective step toward national energy security and environmental sustainability.

Conclusion: Embracing Solar Energy for a Brighter 2026
As Pakistan stands at the crossroads of energy challenges and opportunities, solar energy emerges as the most practical and economically sound solution for households and businesses alike. With electricity prices projected to continue their upward trajectory and solar technology becoming increasingly efficient and affordable, there has never been a better time to invest in solar energy. The potential 18% GST increase on imported solar panels starting January 2026 further reinforces the economic case for acting sooner rather than later.
The journey to energy independence begins with a single step—assessing your energy needs, researching reputable installers, and making an informed decision about the right solar solution for your specific circumstances. While the upfront investment may seem significant, the long-term benefits of reduced electricity bills, protection against tariff hikes, reliable backup power, and reduced environmental impact make solar power one of the smartest investments a Pakistani homeowner or business owner can make in today’s economic climate.
As we look toward 2026, solar power isn’t just an alternative energy source—it’s rapidly becoming a mainstream solution that promises to reshape Pakistan’s energy landscape while putting power back in the hands of consumers. By harnessing Pakistan’s abundant sunlight, we can collectively work toward a future of lower energy costs, greater economic competitiveness, and improved environmental sustainability for generations to come.
Read Also: Future of Renewable Energy in Pakistan 2026: Opportunities and Challenges
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How much can I realistically save on my electricity bill with solar energy in Pakistan?
Most households can reduce their electricity bills by 50-80% with a properly sized solar energy system . Your exact savings will depend on your energy consumption patterns, system size, and whether you opt for net metering. Commercial establishments often achieve even higher savings, particularly if they shift energy-intensive operations to daylight hours.
2. What is the typical payback period for a solar energy system in Pakistan?
Most grid-tied residential solar systems in Pakistan achieve payback within 3-6 years, depending on system size, energy consumption, and local conditions . Commercial systems often see faster returns due to their larger scale and ability to offset demand charges. After the payback period, you effectively get free electricity for the remaining life of the system, which is typically 25+ years for solar panels.
3. Will my solar energy system work during power outages?
This depends on your system type. Basic grid-tied systems automatically shut down during power outages for safety reasons. However, hybrid systems with battery backup can continue providing power during outages. If backup power is important to you, discuss battery storage options with your installer.
4. What maintenance does a solar energy system require?
Solar systems require minimal maintenance. Regular cleaning of panels (especially in dusty areas), periodic visual inspections, and ensuring connections remain tight are typically sufficient. Most quality inverters come with monitoring systems that alert you to any performance issues.
5. How does net metering work in Pakistan?
Net metering allows you to export excess solar electricity to the grid in exchange for credits on your electricity bill. When your system produces more power than you’re using (typically during daytime), the excess flows to the grid and your meter runs backward. At night or during cloudy weather, you draw power from the grid and use your accumulated credits .
6. What happens if I produce more solar energy than I use?
With net metering, excess energy is exported to the grid and you receive credits on your electricity account. These credits are typically carried forward to offset your future grid consumption. Different DISCOs have varying policies on how long credits can be banked and whether there are any limits on export amounts.
7. How long do solar energy typically last in Pakistan’s climate?
Quality solar panels are designed to last 25 years or more. Most manufacturers guarantee that their panels will still produce at least 80% of their original output after 25 years. The extreme heat in parts of Pakistan can slightly accelerate degradation, which is why it’s important to choose panels with good temperature coefficients.
8. Can I expand my solar system in the future if my energy needs increase?
Yes, but planning for future expansion during the initial installation is advisable. With string inverter systems, expansion possibilities may be limited by inverter capacity. If you anticipate needing to expand, consider microinverters or ensure your string inverter has sufficient spare capacity. Also, leave adequate space on your roof for additional panels.
9. Are there financing options available for solar installations in Pakistan?
Yes, several banks in Pakistan now offer green financing options specifically for solar installations. These include Bank of Punjab, HBL, MCB, and others. Terms and interest rates vary, so it’s worth comparing options. Some installers also offer installment plans or lease-to-own arrangements.
10. How do I choose between different types of solar panels?
Consider panel efficiency (especially if you have limited roof space), temperature coefficient (important in Pakistan’s hot climate), warranty terms, and the manufacturer’s reputation. Tier 1 manufacturers typically offer better quality and reliability. Your installer should provide multiple options with clear explanations of the trade-offs between cost and performance.






1 thought on “How to Save Electricity Bills with Solar Energy in Pakistan 2026”